After the introduction of lithography in the late 18th century, several other printing technologies were introduced that improved upon the lithographic process, offering various advantages and benefits for different printing applications.
ROTARY PRESS
In 1843, Richard Hoe patented the first successful rotary press, which used a continuous roll of paper and a rotating cylinder to print at high speeds.
The rotary press is a printing machine that uses a cylindrical printing plate instead of a flat one, allowing for faster and more efficient printing.
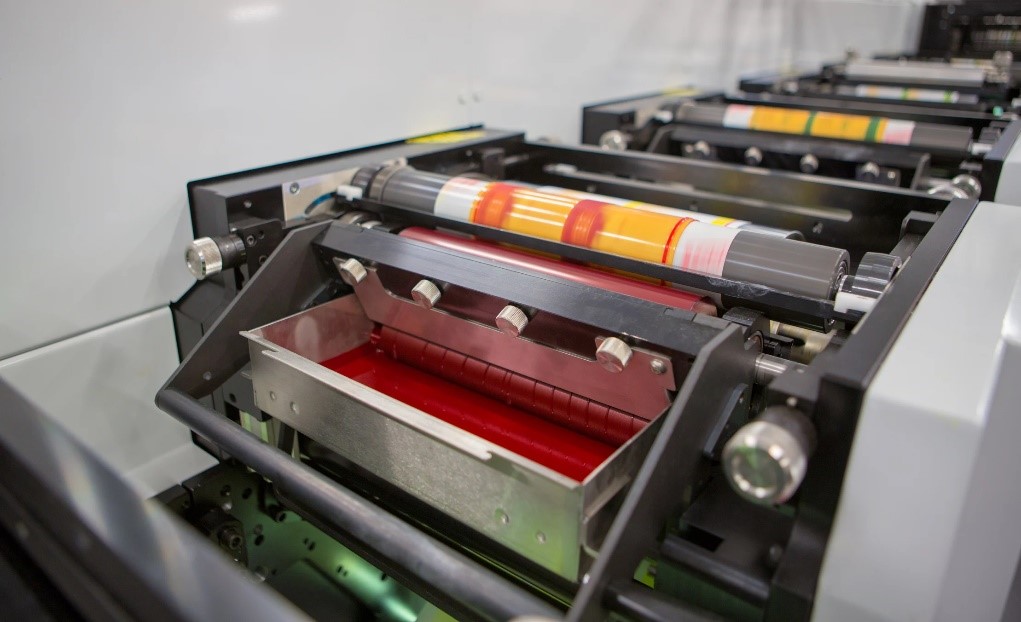
OFFSET PRINTING
This technique is a popular printing method and was developed in 1875 for high-volume commercial printing. It involves transferring ink from a printing plate to a rubber blanket, which then transfers the ink to the paper. Offset printing is known for its high image quality and consistency, and is often used for printing books, magazines, and marketing materials.
FLEXOGRAPHY
Flexography printing is a printing technique that is similar to letterpress printing, but it uses a flexible printing plate instead of a rigid one. This flexibility allows for a wider range of materials to be printed, including plastics, foil, and other non-porous materials. Introduced in 1890, flexography printing is commonly used for printing labels, packaging materials, and newspapers.
SCREEN PRINTING
The technique of screen printing was developed in China between 960 and 1279 AD under the Song Dynasty, but it didn't gain popularity in Europe until the early 1910s when silk material became more widely available. Screen printing is a versatile printing method that can be used on a variety of surfaces, including paper, fabric, and plastic. It involves creating a stencil, or screen, of the desired design, and then using a squeegee to push ink through the screen and onto the printing surface. Screen printing is known for its bold, vibrant colors and its ability to print on a wide range of materials.
INKJET PRINTING
Inkjet printing is used for printing photographs and graphics. It works by spraying tiny droplets of ink onto the printing surface, creating a highly detailed and accurate image. Inkjet printers are known for their affordability and ease of use and were developed in 1951.
LASER PRINTING
In 1969, came along laser printing. Laser printing is a fast and efficient printing method that uses toner rather than ink. It involves using a laser to create an electrostatic image on a photosensitive drum, which then attracts toner particles. The toner is then transferred onto the printing surface and fused to the paper using heat. Laser printing is known for its high speed and precision, and is commonly used for printing documents, marketing materials, and packaging.
DIGITAL PRINTING
1991 saw the emergence of digital printing. It is a printing technology that has gained popularity in recent years due to its ability to produce high-quality images quickly and cost-effectively. Unlike traditional printing techniques, digital printing does not require printing plates or film. Instead, the image is directly printed onto the paper or other materials. Digital printing is ideal for short print runs, customizations, and personalized printing.
3D PRINTING
3D printing is a relatively new printing technology that allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital model. 3D printing uses additive manufacturing, which involves adding material layer by layer to create the final object. 3D printing is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing and production.
Each of these printing technologies has its own unique advantages and applications, and they continue to evolve and improve to meet the ever-changing needs of the printing industry.