Child-resistant packaging comes in a variety of forms, each designed to serve a specific purpose. Some popular options include: Along with convenience and accessibility, child-resistant packaging has become a vital tool in preventing accidental ingestions and ensuring safety for parents, caregivers, and even businesses. This blog dives into the world of child-resistant packaging, examining its various options, industry standards, and emerging trends that contribute to the well-being of children.
Types of Child-Resistant Packaging
1.
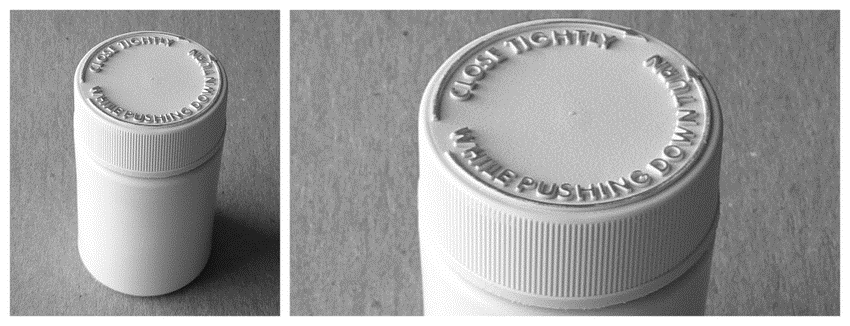
- Push-and-turn caps: These lids require a combination of dexterity and force to open, making them challenging for young children.
- Blister packaging: Commonly used for pharmaceuticals, blister packs keep pills safely enclosed, requiring pushing through the foil to access the contents.
- Slide and squeeze containers: Commonly used for liquid medications, these containers demand precise manipulation to dispense their contents.
- Resealable pouches with child-resistant zippers: These flexible packages often house edibles or medications and feature a locking mechanism that thwarts easy entry.
- Child-resistant bags: Frequently used in the cannabis industry, these bags require specific actions like pinching and pulling to open.
- Child-resistant boxes: These robust packaging solutions are used for a variety of products, requiring advanced motor skills to access their contents.
Key Features of Child-Resistant Packaging
Tamper-evident closures: These mechanisms make it clear if the package has been opened, providing an added layer of security.
Compliance with regulatory standards: Child-resistant packaging must meet specific guidelines and standards set forth by organizations like the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and ASTM International.
Accessibility for adults: While challenging for children, these packages should be reasonably accessible for adults.
Testing and certification: Products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet child-resistant standards, often gaining certifications to prove their effectiveness.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Child-resistant packaging is heavily regulated and monitored by organizations like the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and is governed by laws such as the Poison Prevention Packaging Act (PPPA). These entities set forth stringent requirements and conduct regular inspections to guarantee safety.
India, currently, DOES NOT have any specific regulations for child-resistant packaging.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Safety benefits: These packages effectively reduce the risk of unintentional ingestions, offering peace of mind to parents and caregivers.
User-friendliness: Some forms of child-resistant packaging may pose challenges for adults as well, potentially leading to frustration.
Environmental concerns: The use of plastics and complex packaging can have environmental impacts, which is a growing concern.
Cost considerations: Implementing child-resistant packaging can increase production costs, which may be passed on to consumers.
Emerging Trends
Sustainable materials: A shift towards eco-friendly materials that protect both children and the environment.
Smart packaging solutions: Incorporating technology for added security and convenience.
Customization options: Tailoring packaging to specific products and user preferences.
User experience enhancements: Focusing on ease of use for adults while maintaining child-resistant qualities.
Choosing the Right Packaging
Selecting the appropriate child-resistant packaging is crucial and depends on the nature of the product. Considerations for various industries, including pharmaceuticals, household chemicals, cannabis, and more, are essential in making informed decisions.
Child-resistant packaging isn't just a safety precaution; it's a necessity. With evolving industry standards, innovative trends, and a growing array of packaging options, child-resistant packaging is evolving to protect the ones we cherish most. As we move forward, we must continue to prioritize child safety while adapting to changing needs and preferences.