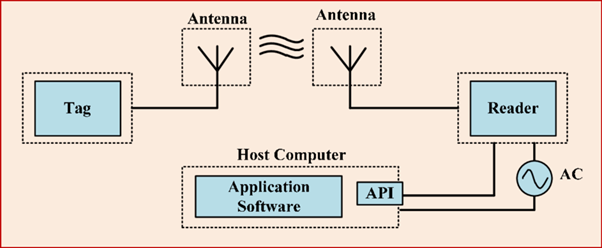
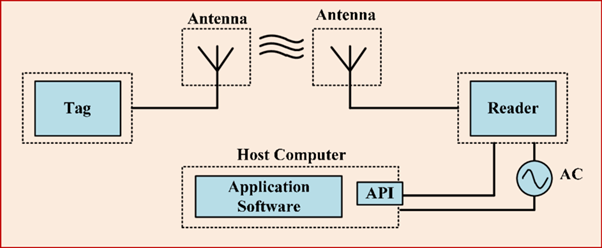
What is RFID?
Radio Frequency Identification Device (“RFID”) is a technology that uses radio-frequency waves to transfer data between a reader and a movable item to identify, categorize and track.
How does it work?
An RFID Tag Consists of:
- An antenna that detects radio waves and responds with signals
- A chip that stores and manipulates data
RFID Reader kit consists of:
- Radio circuitry (RFID Antenna) for generation and detection of radio waves
- Computational device for basic processing and filtering of signals
- Software library deployed on a PC interacting with Reader device
An RFID recognizes frequencies ranging from 125KHz (LF) to 915MHz (UHF). The reader emits a radio signal that activates the tag and reads and writes data to it. As products are shipped, received, or stored, the information can be read and received by the reader.
What are the advantages of RFID?
- RFID is fast, reliable, and does not require physical sight or contact between the reader/scanner and the tagged item.
- The process of utilizing RFID allows a company to improve its business processes, such as inventory management and supply chain management, through reduced labor costs, errors, and handling costs. With more timely and accurate answers to inventory control, companies can run much more efficient forecasting, production, and distribution operations. It allows companies to know exactly where their inventory is, how much of it is on hand, and when to re-order or supply.
- Unlike other methods of automatic identification (auto-ID) where items must be physically separated or read individually, numerous RFID smart label transponders can be read simultaneously – identifying multiple labels, containers, or items all at the same time as they pass a reading location or are read with a handheld scanner.
What are the types of tags?
There are two basic types of tags:
Active
- Tag transmits radio signal
- Battery powered memory, radio & circuitry
- High Read Range (750 feet)
Passive
- Tag reflects radio signal from the reader
- Reader powered
- Shorter Read Range (4 inches - 20 feet)
Tags can also be read-only or rewritable.
What are the types of RFID readers?
- A handheld reader
- A long-range reader
- A wrist-watch reader
What are some applications of RFID?
- Badges/Smart keys
Grant or deny access
- Agriculture
Livestock Tracking
- Toll roads
Tracking and charging
- Asset Management
- Maintenance
Aircraft – Intelligent Toolbox
Equipment – Record database on Tag
- Supply Chain Management
Inventory control
Logistics
To learn more about RFID and its associated technology, Full presentation on Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is now available on demand..