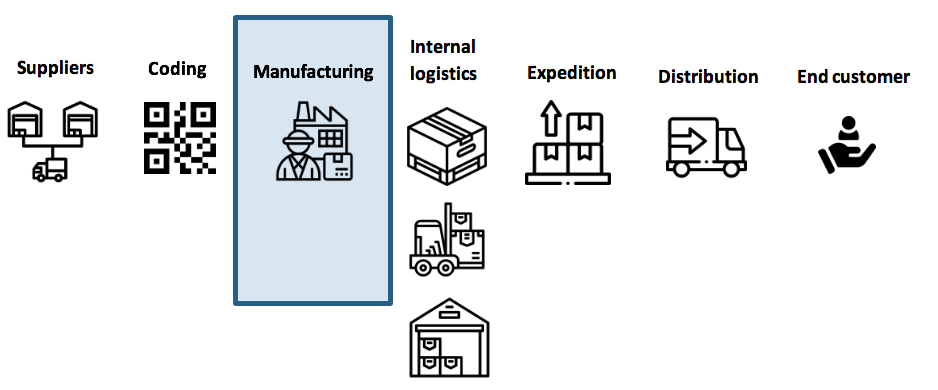
Types of traceability Four different types/stages can be distinguished in the life of a product, depending on the type of business or product to be traced: Raw materials: identification of the components that make up the product Production/verification: until we get our final product Packing/Aggregation: from the completed unit through to its final packaging Logistics: from shipment to the end user Shall we define traceability? Traceability is the ability to retrieve the full history or location of an item or product by means of recorded identification. All in all, to register all the information of a product, such as manufacturers, suppliers, distributors. This information is tracked in all processes, from raw material allocation, processing, handling, assembly to distribution and sale. Types of traceability Four different types/stages can be distinguished in the life of a product, depending on the type of business or product to be traced: Raw materials: identification of the components that make up the product Production/verification: until we get our final product Packing/Aggregation: from the completed unit through to its final packaging Logistics: from shipment to the end user traceability Traceability in the production process This is also called internal traceability, and is the most important of those previously mentioned when it comes to the creation or transformation of a product. Thanks to this information, it is possible to retrieve the complete historical record of a product through its internal processes, including its handling, its composition, the machinery used, its schedule, its temperature, its batch, etc. In other words, all the indicators that make or may make the product stand out for the end user. The aim is to be able to record information from each stage of production. The production/assembly/transformation phases may vary, but in all of them we can store the following information: Operator Start time Duration Assembled components (supplier/batch) Verification test Machine code Incidents This process involves marking the individual product with a unique code, which we call serialization, and identifying it in each of the production processes. Throughout the manufacturing process of the product or item it may also be necessary to add different raw materials in order to complete it, and consequently these must be identified and correctly coded in order to be registered. All this data can be entered manually or automatically, depending on the production line. Benefits of internal traceability A well-executed traceability system in the production process brings great benefits, such as Optimization in the supply chain, meaning more efficient management in logistics. Increased productivity, as it is possible to know the output per machine, time per phase / stage / product. Complaint and recall management, meaning that possibly defective items can be located Prevents counterfeiting A better service to the end user